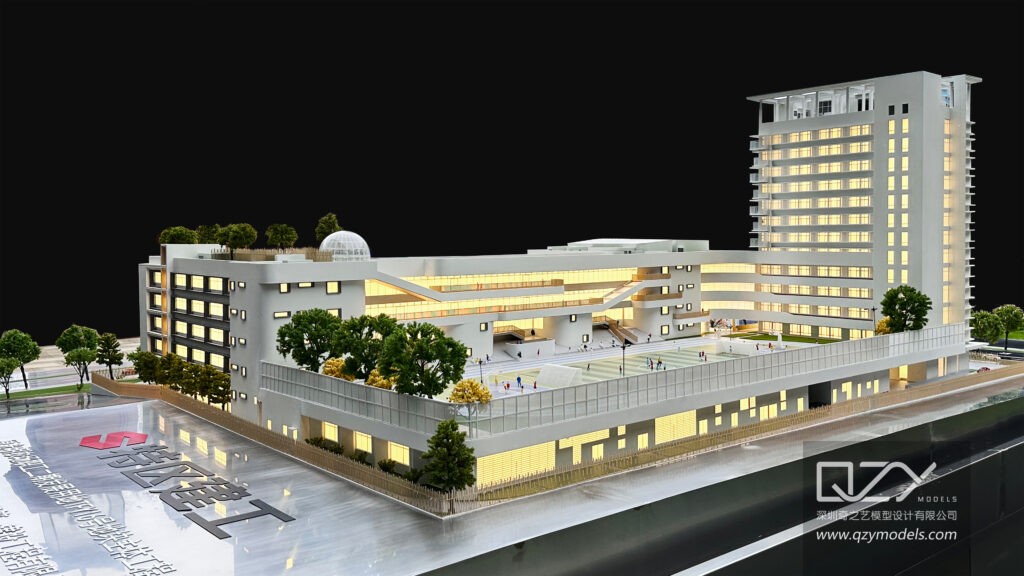
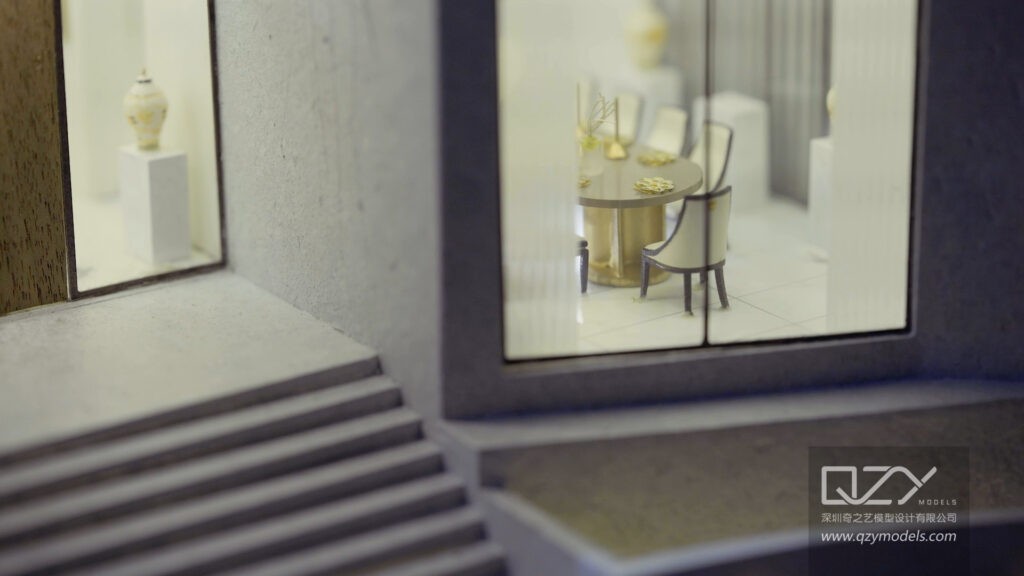
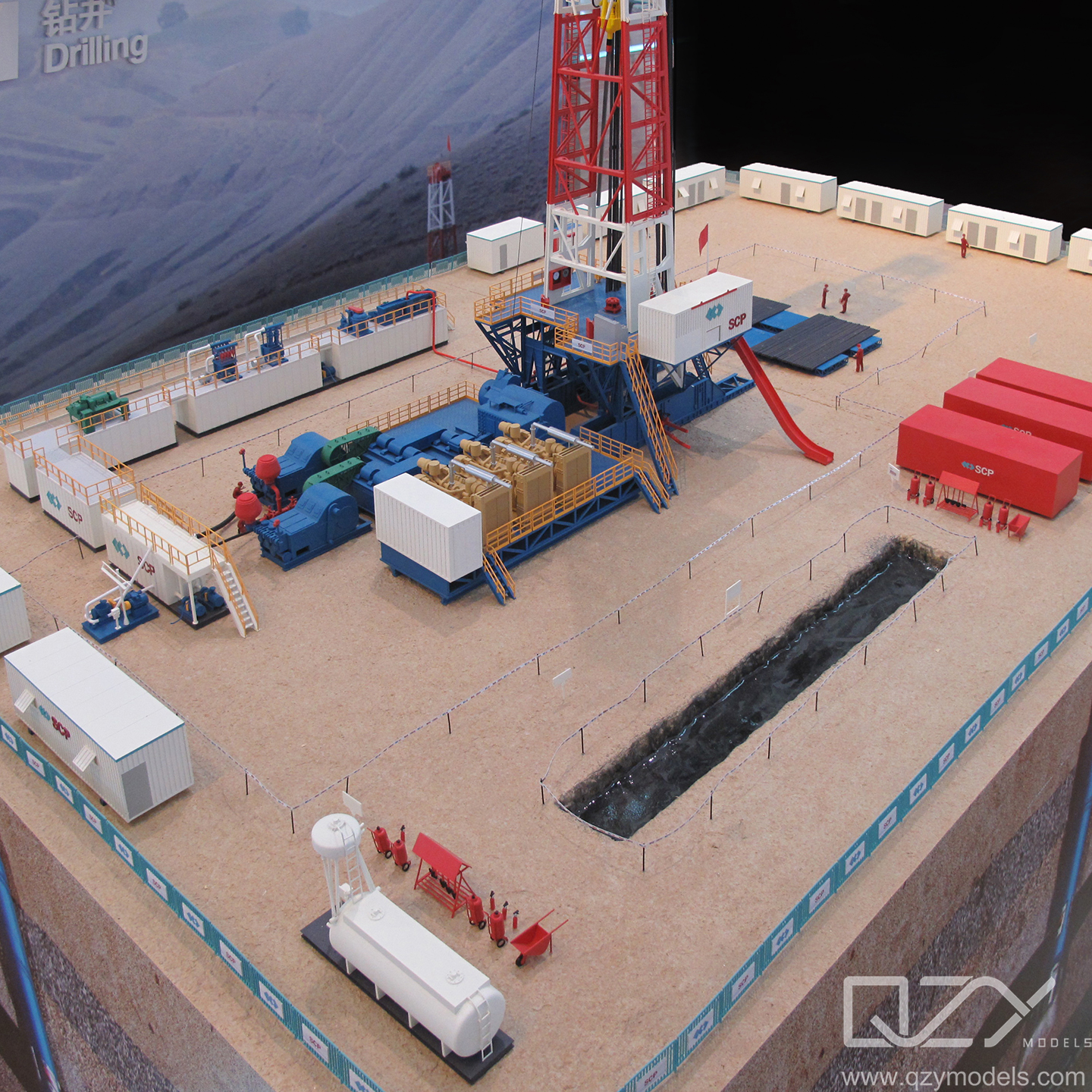
As the information age progresses, education and cultural communication undergo significant transformations. The fusion of diverse cultures emphasizes the growing importance of interdisciplinary learning. Simultaneously, the rise of new media challenges traditional education models. In response, physical models emerge as an innovative tool, using multisensory presentations to enrich both exhibitions and instructional content. This dynamic combination not only addresses traditional education’s shortcomings but also meets the evolving demands of cultural communication. The integration of physical models with new media offers a more vivid, three-dimensional approach, providing students with immersive cultural experiences and fostering deeper interdisciplinary understanding.
The role of physical models in cultural education

Physical models in cultural education not only offer visual learning tools but also create immersive learning experiences. This approach enhances students’ understanding of cultural knowledge, sparking a deep interest and promoting innovation in cultural education.
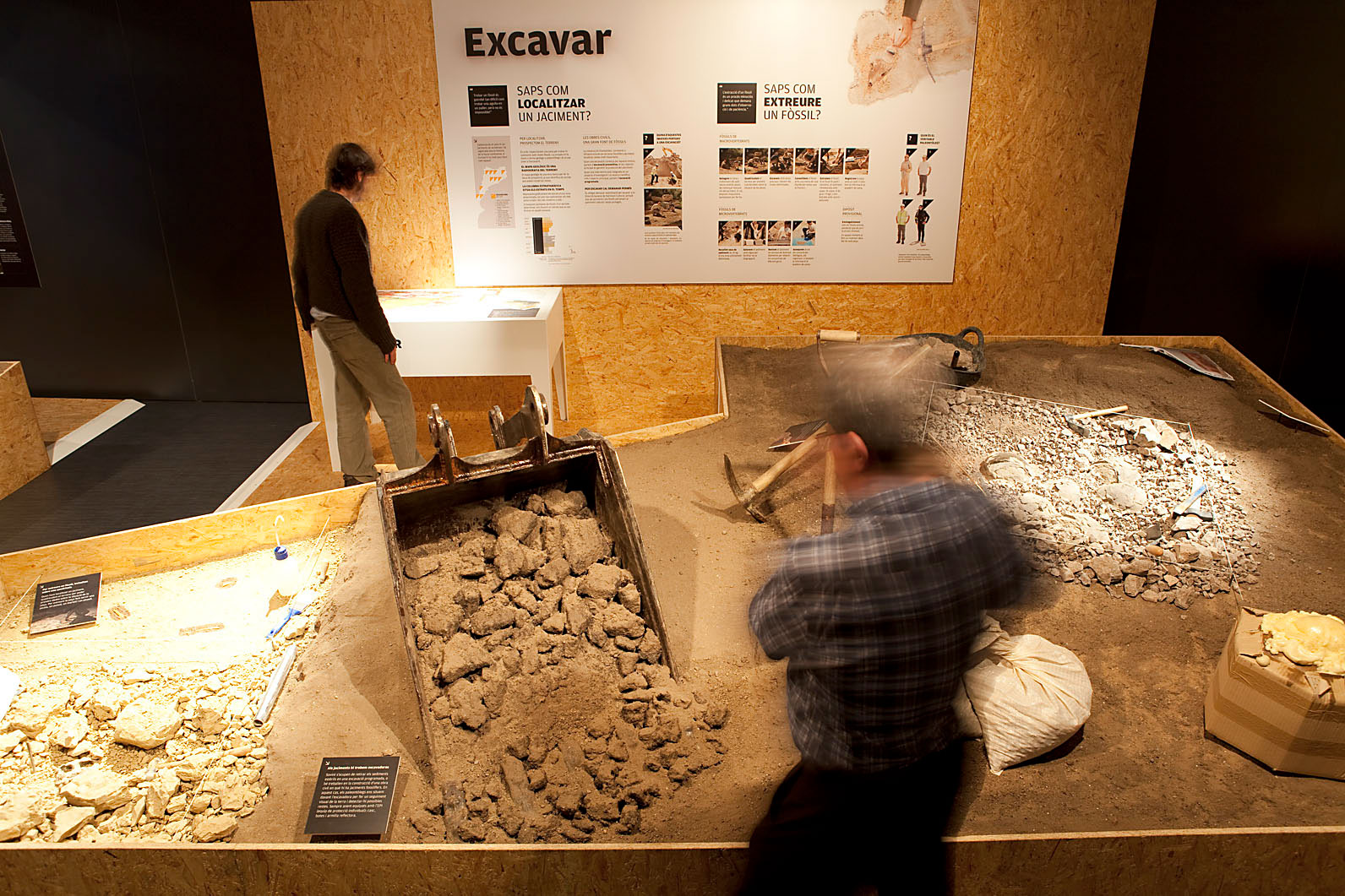

1、History & Archaeology
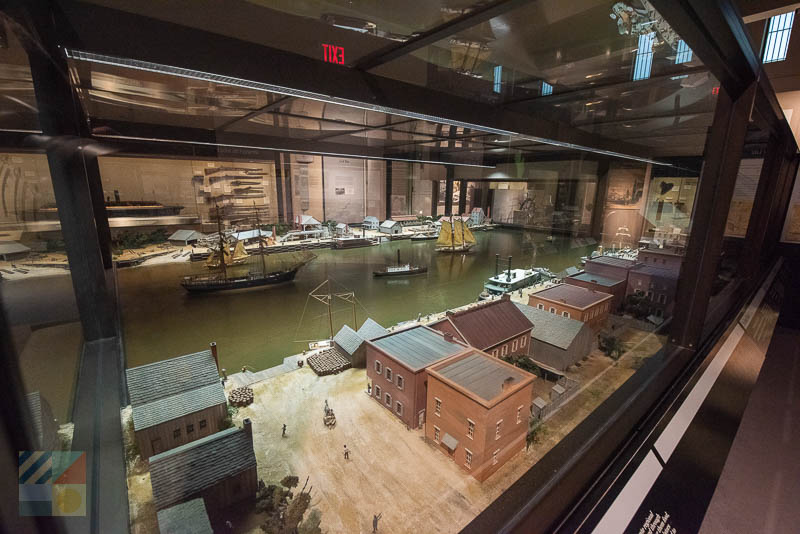

In history education, physical models play a crucial role in recreating ancient architecture and artifacts. These models, such as wooden replicas of architectural structures or 3D-printed versions of historical sites like the Roman Colosseum, provide students with a more tangible and interactive learning experience. Unlike rare original artifacts, these replicas are more accessible and help students grasp the architectural styles and social structures of ancient civilizations. Additionally, practical learning activities, such as simulating archaeological excavations, deepen students’ understanding of history and archaeology, exposing them to the complexities of excavating and organizing artifacts.
2、 Art & literature
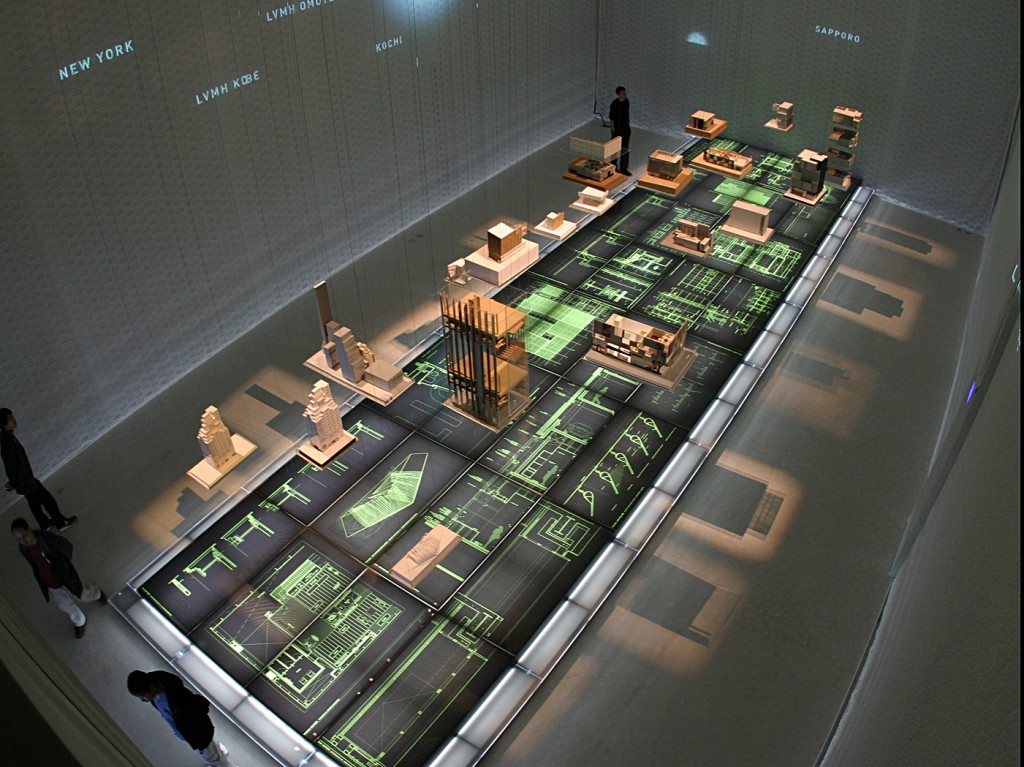

The use of physical models enhances students’ perception of artworks and literature while fostering their aesthetic and literary appreciation in multiple dimensions. Art museums employ physical models to showcase the three-dimensional details of artworks, providing a deeper understanding for viewers. For example, magnifying details or reconstructing damaged pieces through models enhances the art appreciation experience and adds interest to art education. In literary education, presenting key scenes of works in model form allows students to grasp the plot and background from a more immersive perspective.
3、Society & Folklore Studies

Through physical models, students gain insight into diverse societies’ spatial structure and social organization. For instance, simulating ancient city layouts in small-scale models allows students to grasp the hierarchy and functional divisions in societies visually. This hands-on learning aids in understanding urban development across different regions and periods. Additionally, physical models can simulate traditional folk rituals, enhancing students’ comprehension of cultural traditions and beliefs, and broadening their awareness of cultural diversity.
Application scenarios of physical models in cultural communication
1、Museums & exhibitions

Physical models in the exhibition field offer diverse and immersive scenarios, providing audiences with a visually engaging and interactive experience. Physical models convey the details and scenes of civilizations intuitively through sequential replication of ancient buildings, artifacts, and historical events, allowing audiences to authentically experience cultural content. In knowledge-intensive exhibitions, particularly in fields like medicine, biology, agriculture, and technology, specialized model scene designs enhance the exhibition’s three-dimensional and dynamic aspects beyond flat visualization. Moreover, combining physical models with augmented reality technology enables virtual interactions with exhibition objects, attracting more visitors and enhancing cultural communication’s appeal and educational value.
2、Film & Media
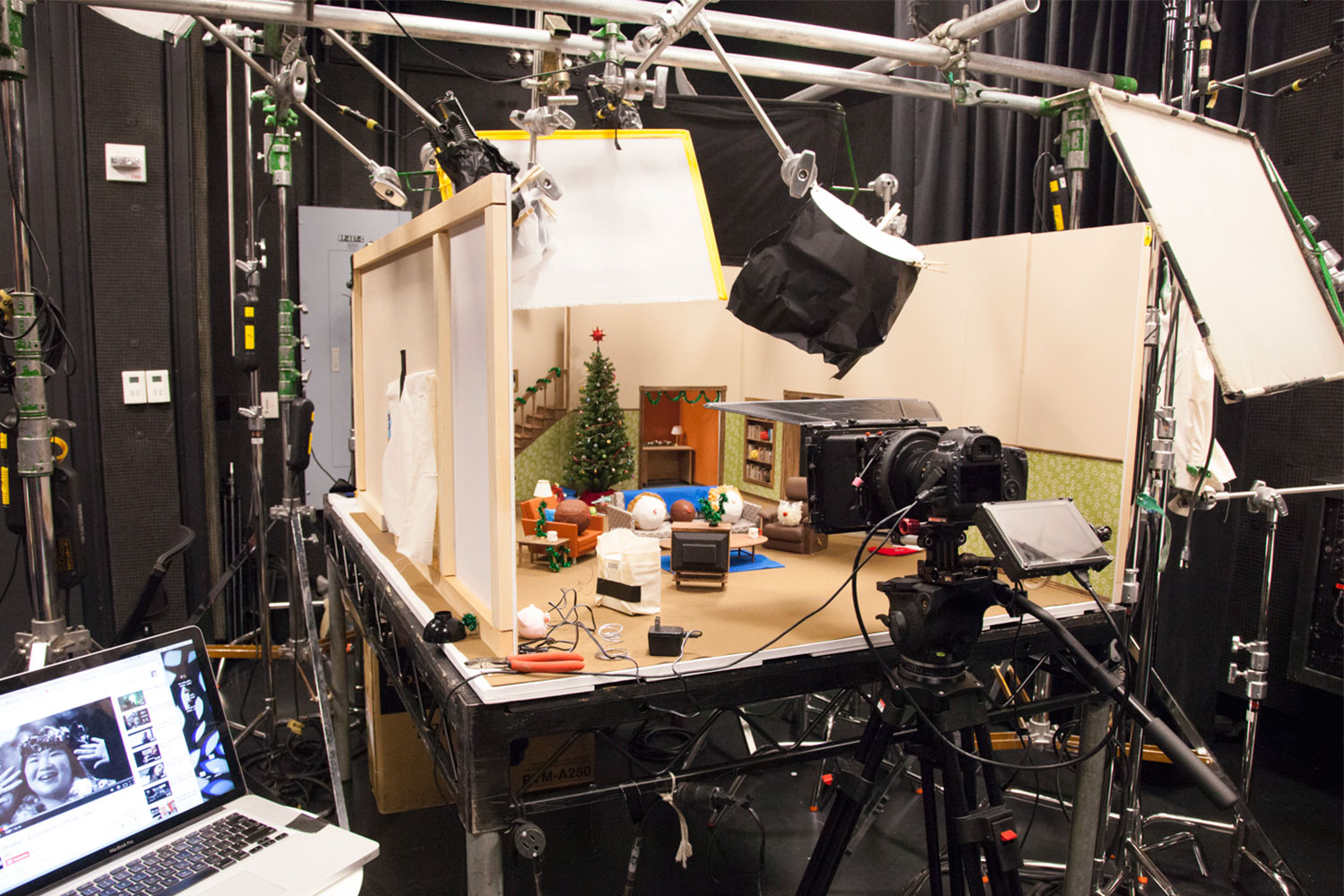

In film production, special effects physical models, such as those depicting extraterrestrial beings or futuristic cities in science fiction films, play a crucial role in creating realistic and captivating scenes. In artistic programs and documentaries, model scenes are employed to recreate complex historical events or cultural phenomena, enhancing expressive forms and deepening the audience’s understanding of intricate subjects. Furthermore, in the realm of film and media, physical models enhance the artistic quality by accurately reconstructing specific historical architectural or scenic elements. Model props, detailing ancient buildings, utensils, weapons, etc., contribute to the overall authenticity of the work.
The Value Presentation of Physical Models in the Cultural Field
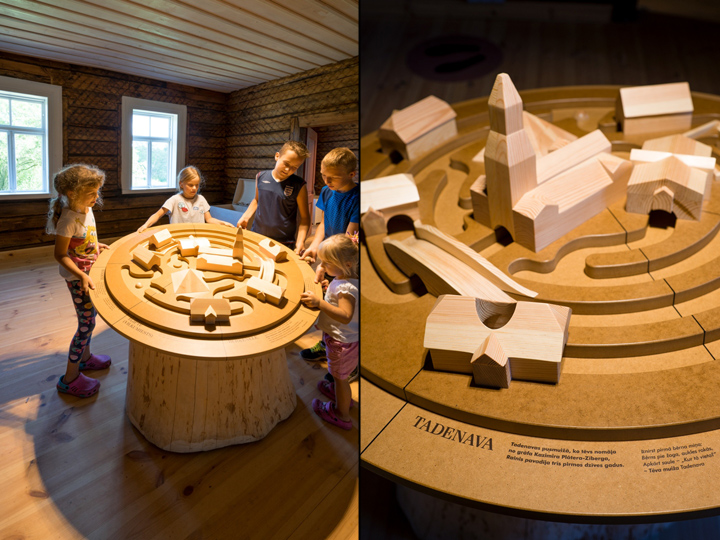

Physical models are essential tools in cultural education and communication, aiding in understanding the past, enriching art displays, promoting cultural heritage, and enhancing audience interaction. These applications not only broaden cultural education but also provide concrete avenues for interdisciplinary understanding. By conveying cultural information, physical models guide people to contemplate the deeper layers of cultural significance. In the future, with technological advancements, their application in the cultural domain will expand, offering even more diverse and enriched cultural experiences.
- The pictures come from the Internet and co-editors. If there is any infringement, please contact us and we will delete and rectify it immediately.