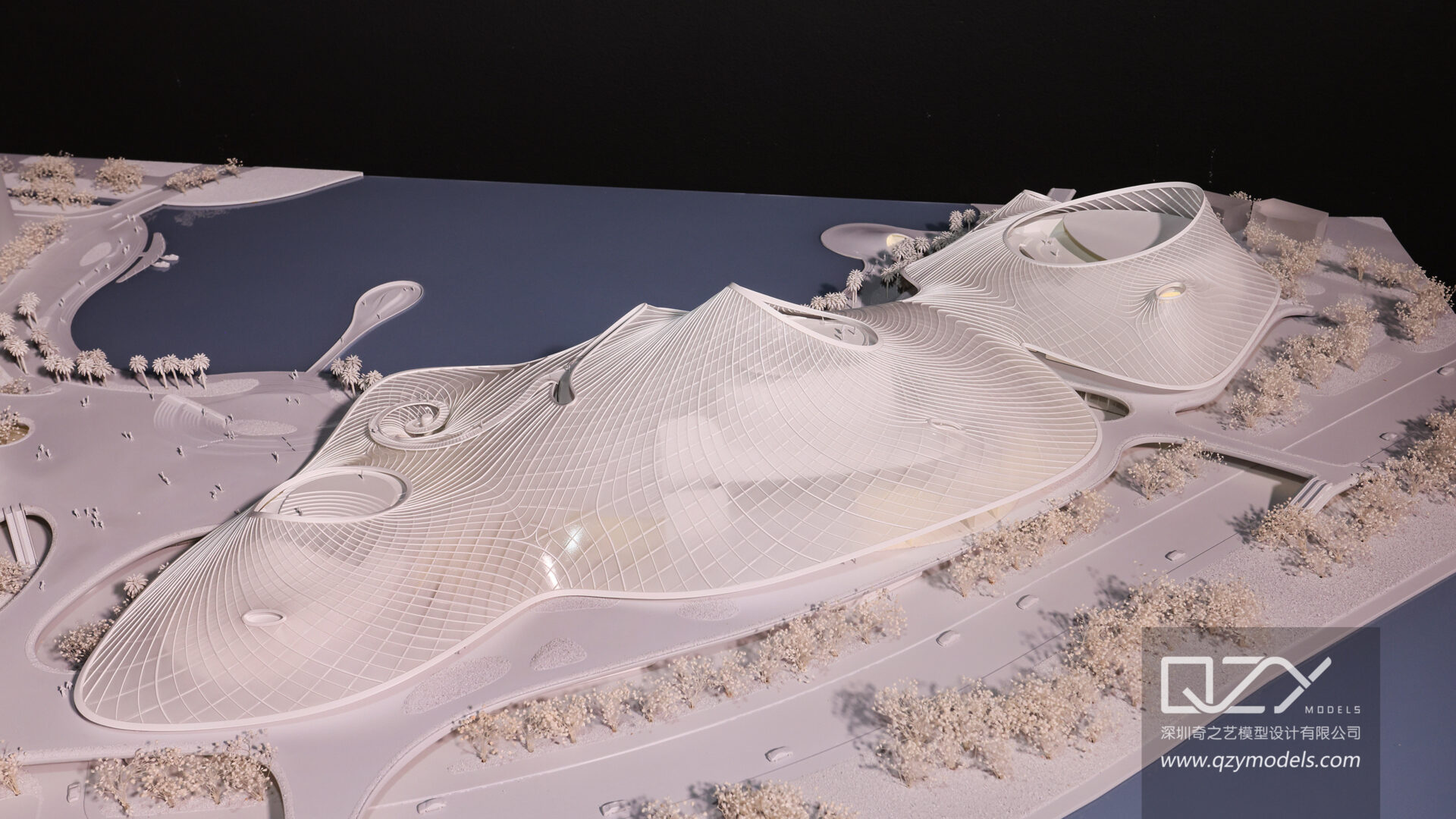
In the ever-evolving landscape of architectural representation, the advent of 3D printing has ushered in a new era of precision and innovation. This article delves into the realm of 3D-printed architectural models, exploring their purpose, the techniques involved, and the transformative impact they have on architectural visualization and communication.
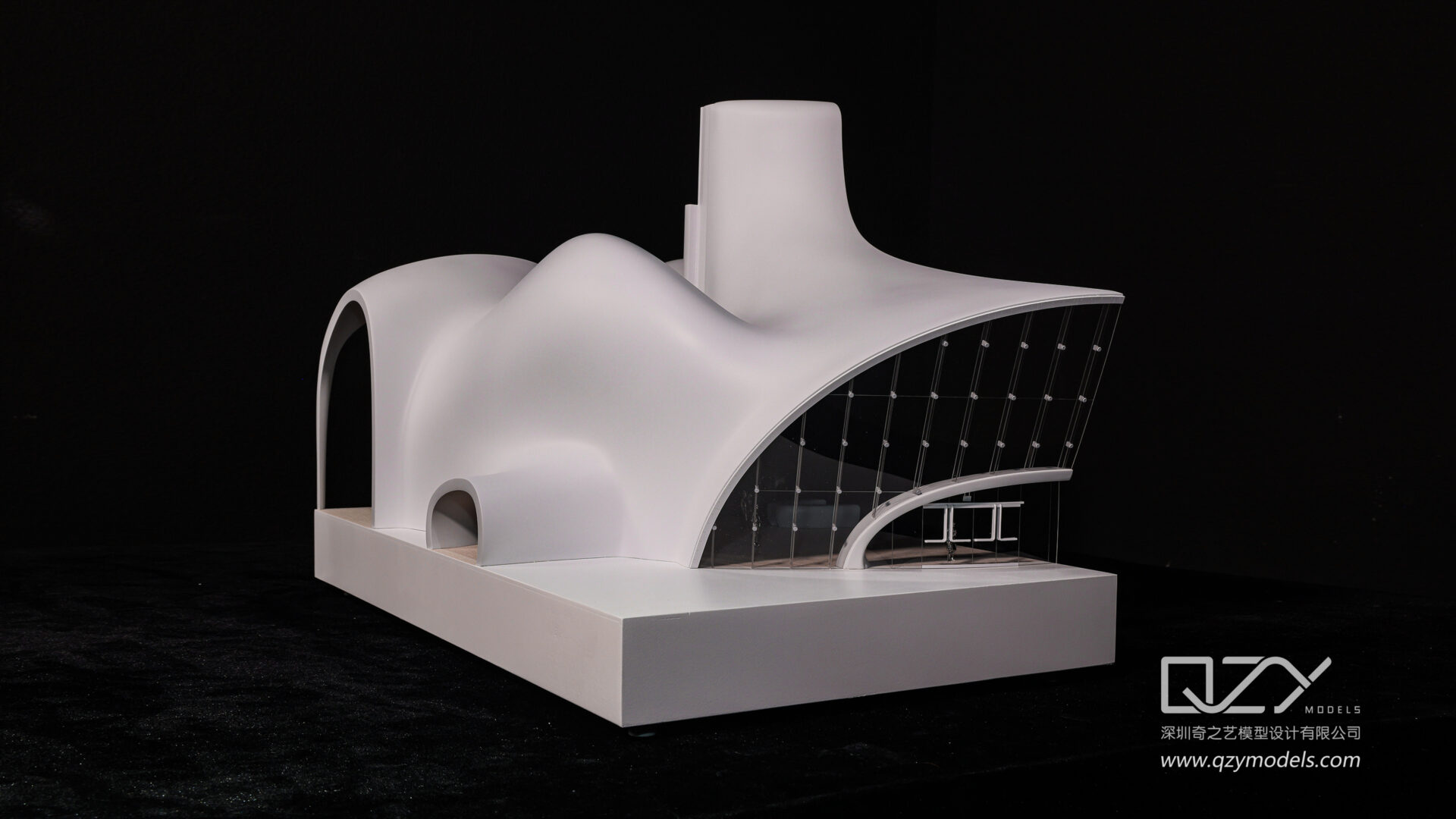

I. The Purpose and Significance of 3D Printed Architectural Models
- A. Precision in Design Communication:
3D-printed architectural models serve as powerful tools for precisely communicating design intent. Unlike traditional models, these three-dimensional replicas offer a level of detail and accuracy that transcends the limitations of conventional model-making techniques, providing stakeholders with a tangible representation of architectural visions.
- B: Enhanced Client and Stakeholder Engagement:
The tactile nature of 3D printed models enhances client and stakeholder engagement by providing a hands-on experience. Clients can physically interact with scaled replicas, gaining a deeper understanding of spatial relationships, design features, and overall project aesthetics. This heightened engagement fosters more informed decision-making and collaboration.
II. Techniques and Methodologies in 3D Printing Architectural Models
- A: Digital Modeling and Rendering: The process begins with the creation of a digital model using architectural design software. Architects and designers meticulously refine the digital representation to ensure accuracy. This digital model serves as the foundation for the subsequent 3D printing process.
- B: Layer-by-Layer Construction: 3D printing relies on layer-by-layer construction, with the model being built up gradually from the bottom. This additive manufacturing process allows for intricate detailing, capturing the nuances of architectural elements with precision. Various printing materials, including plastics, resins, and even metals, can be employed depending on the desired result.
III. Detailing in 3D Printed Architectural Models
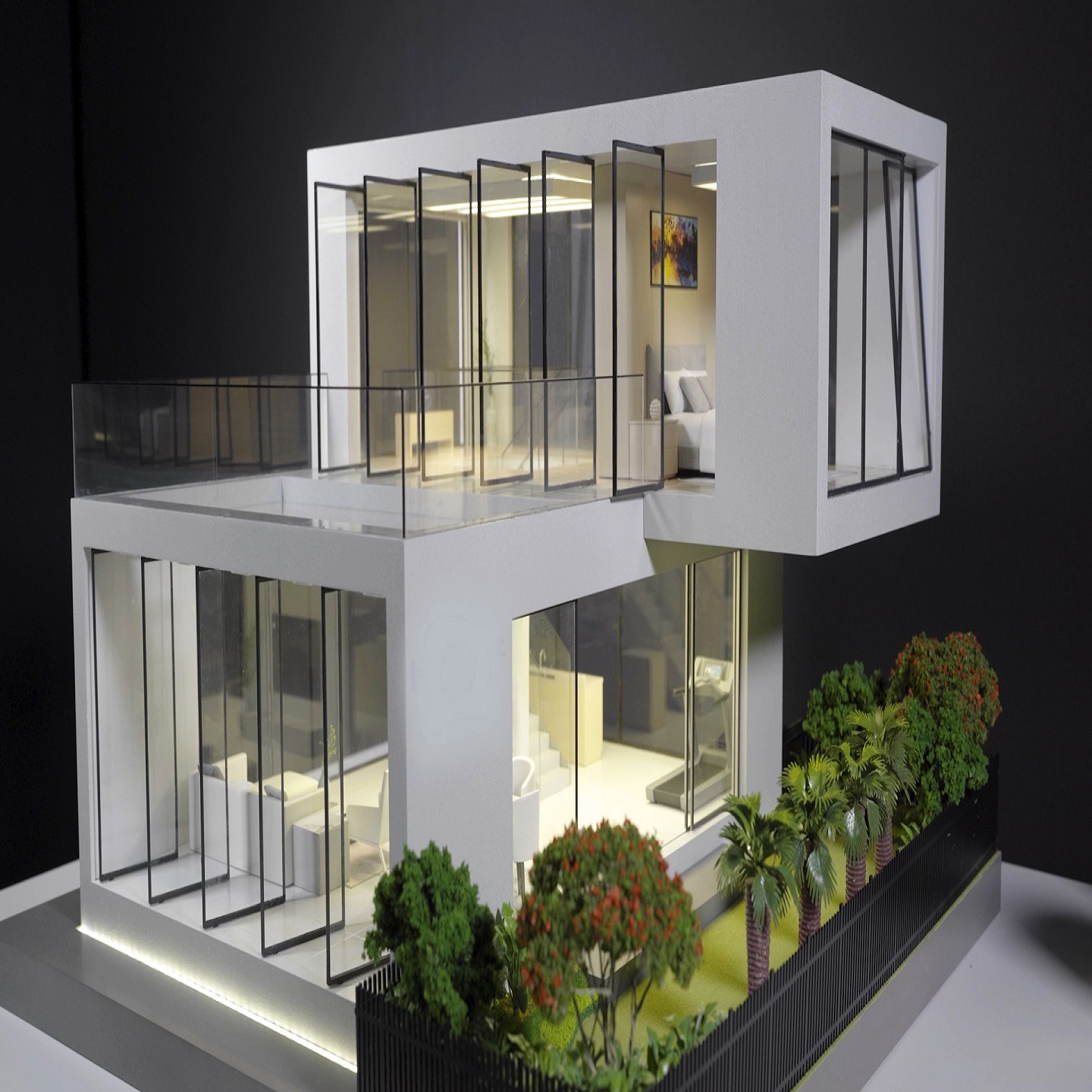
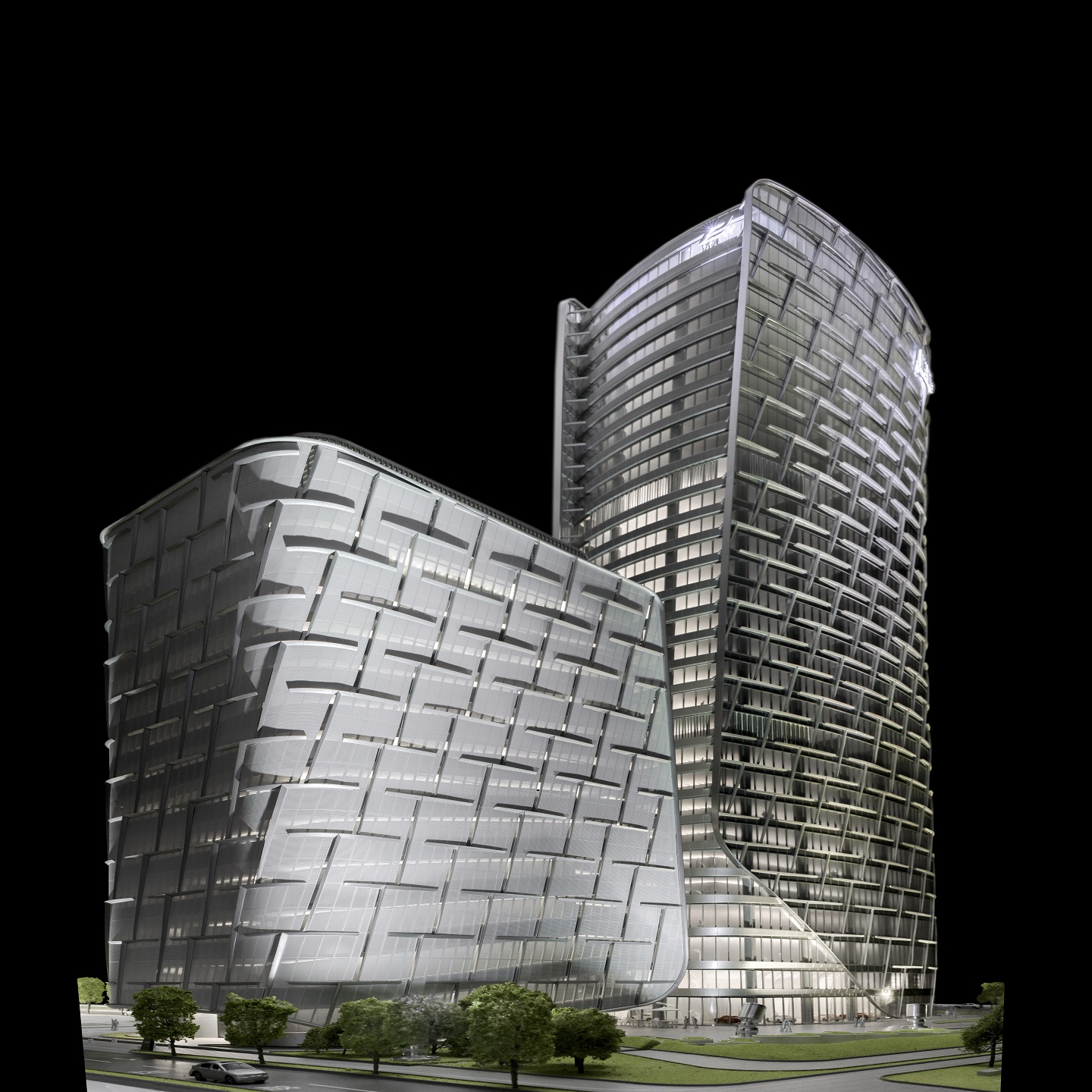
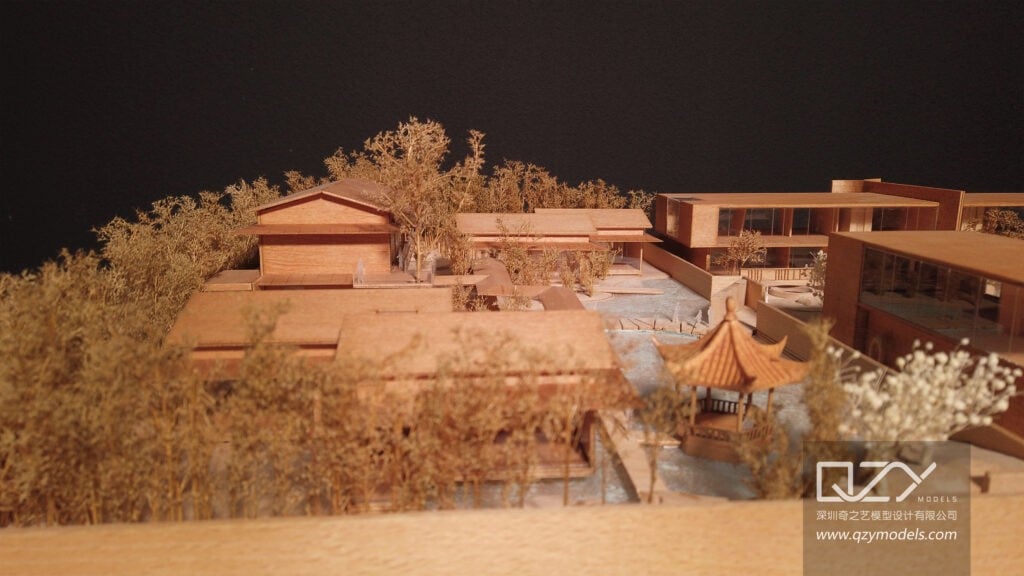
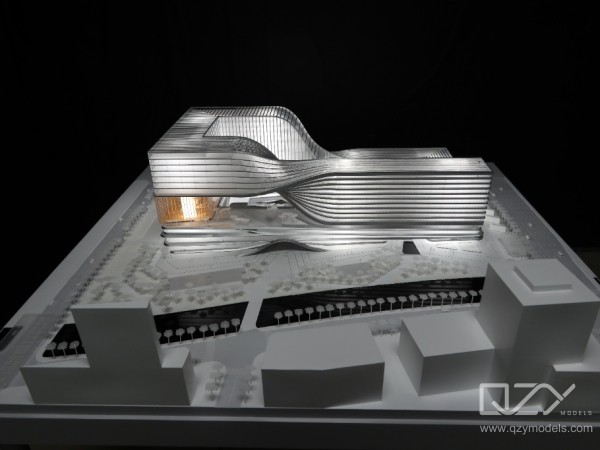
- A: Microscopic Precision: One of the defining features of 3D printed architectural models is the microscopic precision achievable in detailing. Fine textures, intricate facades, and delicate features can be reproduced with accuracy, offering a level of realism that was previously challenging to attain through traditional model-making techniques.
- B: Textures and Material Realism: Beyond structural details, 3D printing excels in replicating textures and material realism. From the smooth surfaces of modern buildings to the intricate detailing of historical facades, the technology allows for the faithful reproduction of a wide range of materials, contributing to a more authentic representation of the intended design.
IV. Applications and Impact in Architectural Visualization
- A: Iterative Design Process: 3D printed architectural models facilitate an iterative design process. Architects can quickly produce physical prototypes, allowing for rapid design iteration and refinement. This dynamic workflow enhances creativity, problem-solving, and the exploration of design alternatives throughout the architectural planning stages.
- B: Presentations and Client Pitching: 3D printed models have become integral tools for presentations and client pitching. The tangible nature of these models enhances the clarity of design presentations, providing clients with a visceral understanding of the proposed structure. This visual impact aids in conveying design concepts more effectively than traditional renderings.
V. Future Frontiers and Advancements in 3D Printing Technology
- A: Integration of Augmented Reality: The future of 3D printed architectural models involves increased integration with augmented reality (AR) technology. This allows stakeholders to interact with virtual elements superimposed on the physical model, providing an immersive and dynamic experience. The fusion of 3D printing and AR enhances the depth of architectural visualization.
- B: Sustainable Materials and Practices: As environmental considerations become paramount, the 3D printing industry is exploring sustainable materials and practices. The use of eco-friendly materials and additive manufacturing processes that minimize waste align with the broader trend toward sustainability in architecture and design.
VI. Challenges and Considerations in 3D Printing Architectural Models
- A: Cost Considerations: While 3D printing technology has become more accessible, cost considerations remain a factor. High-quality printers and materials can incur significant expenses, influencing the feasibility of 3D printing for certain projects. However, advancements in technology are gradually mitigating this challenge.
- B: Scale and Size Limitations: The scale and size limitations of 3D printers can pose challenges for printing large or complex architectural models in a single piece. Model-makers may need to divide larger structures into manageable sections, necessitating meticulous assembly to maintain accuracy.
- C: Skill Development and Training: Adopting 3D printing for architectural models requires a shift in skill sets. Architects and model-makers need training in digital modeling software, 3D printing technologies, and material selection. Ensuring a proficient workforce capable of harnessing the full potential of 3D printing is crucial.

3D printed architectural models have emerged as transformative tools, revolutionizing the way architects communicate, collaborate, and visualize their designs. The marriage of digital precision and tangible representation offers unparalleled benefits in design iteration, client engagement, and architectural visualization. As technology continues to advance, the impact of 3D printing on architectural representation is poised to shape the future of the industry, ushering in a new era of innovation and creativity.
Discovering the World Through Miniatures – About Us
QZY Models, founded in 2013 in Shenzhen, China, is a leading professional team specializing in the design and production of customized physical models. Rooted in the architecture industry, QZY Models caters to diverse model production needs, ranging from furniture, interior design, and architectural landscape, to urban planning. Moreover, we are continuously exploring various fields, including dynamic mechanical models, industrial equipment displays, scientific and technological principle displays, and exhibition displays, to create a diverse model service ecosystem.
Since commencing our independent business in 2013 and establishing our base in Shenzhen, ensuring quality has always remained our top priority. We have forged strong collaborations with renowned companies in over ten countries, such as the United Kingdom, the United States, Canada, and Singapore. Our completed projects span across China, the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Poland, Morocco, Ethiopia, and other countries. Presently, QZY Models has established branches or offices in Egypt, Morocco, Saudi Arabia, Lebanon, Italy, the Netherlands, and other locations, firmly committed to serving global customers.
For more information, please visit our official website: www.qzymodels.com.